
Medieval Greek is the link between this vernacular, known as Koine Greek, and Modern Greek. The conquests of Alexander the Great, and the ensuing Hellenistic period, had caused Greek to spread to peoples throughout Anatolia and the Eastern Mediterranean, altering the spoken language's pronunciation and structure.
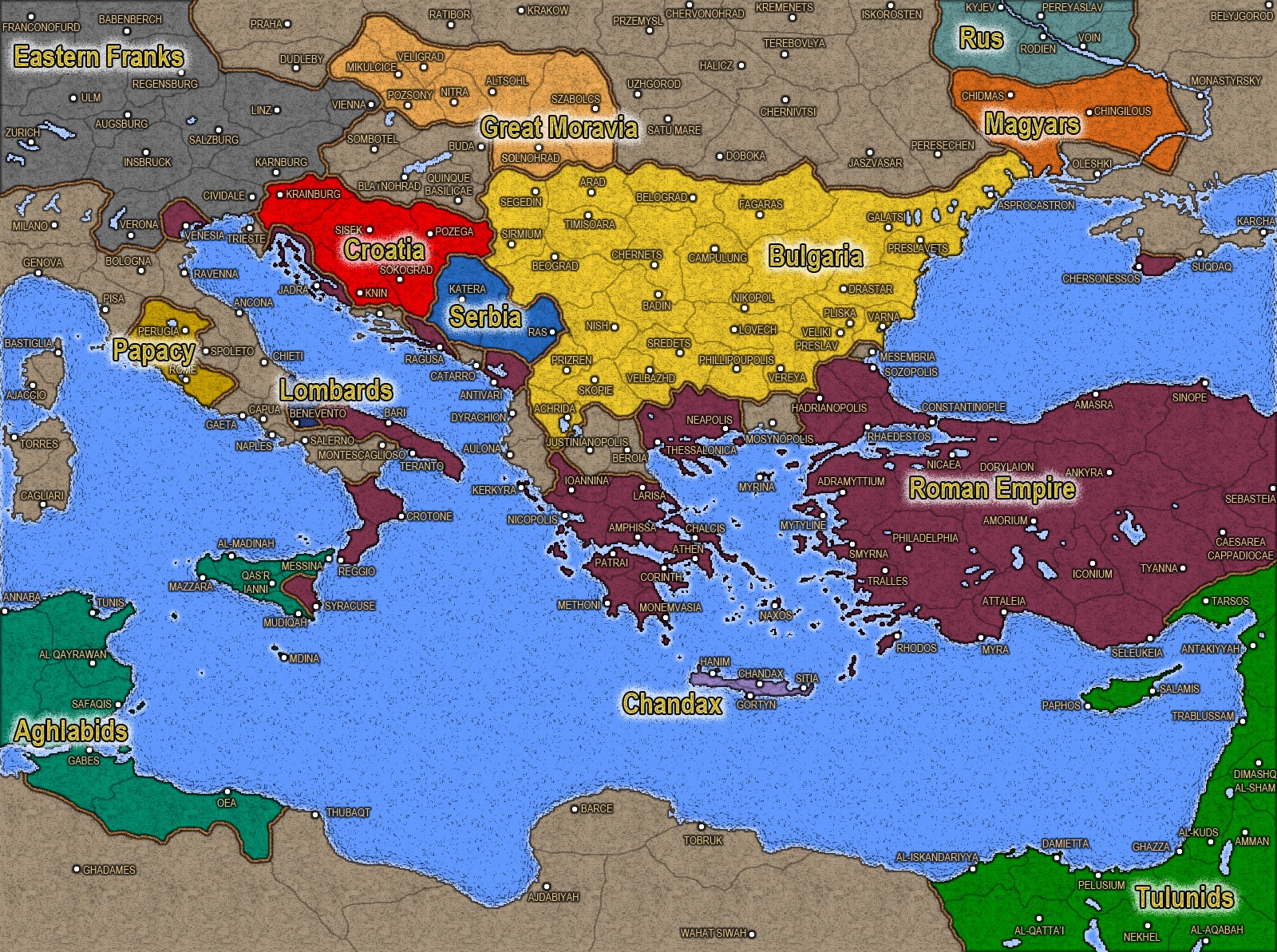
Indeed, by this time the spoken language, particularly pronunciation, had already shifted towards modern forms. However, this approach is rather arbitrary as it is more an assumption of political, as opposed to cultural and linguistic, developments. The beginning of Medieval Greek is occasionally dated back to as early as the 4th century, either to 330 AD, when the political centre of the Roman Empire was moved to Constantinople, or to 395 AD, the division of the empire. The study of the Medieval Greek language and literature is a branch of Byzantine studies, the study of the history and culture of the Byzantine Empire. This stage of language is thus described as Byzantine Greek. Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek or Byzantine Greek) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of Classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople in 1453.įrom the 7th century onwards, Greek was the only language of administration and government in the Byzantine Empire.

For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols instead of Unicode characters. This article contains IPA phonetic symbols.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
